How to operate a drone is a question many ask, and the answer unfolds across a spectrum of skills and knowledge. From pre-flight checks and safety protocols to mastering advanced flight maneuvers and capturing stunning aerial photography, this guide provides a structured pathway to becoming a proficient drone pilot. We’ll cover everything from understanding airspace regulations and basic controls to optimizing camera settings and troubleshooting common issues, ensuring you’re equipped to confidently take to the skies.
This comprehensive guide breaks down the process into manageable steps, making it accessible for beginners while offering valuable insights for experienced users looking to refine their skills. Each section builds upon the previous one, allowing you to progress at your own pace and develop a solid understanding of safe and effective drone operation.
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures
Before embarking on any drone flight, a thorough pre-flight checklist and adherence to safety procedures are paramount. Neglecting these steps can lead to accidents, damage to property, and legal repercussions. This section details the necessary checks and safety considerations.
Drone Inspection
A comprehensive pre-flight inspection is crucial for ensuring safe and reliable operation. This involves checking various components to identify any potential issues before takeoff.
| Component | Check | Component | Check |
|---|---|---|---|
| Propellers | Inspect for damage, cracks, or debris. Ensure they are securely fastened. | Battery | Check battery level and ensure it’s properly connected. Verify the battery health through the drone’s app or indicator. |
| Motors | Visually inspect for any signs of damage or wear. Listen for unusual noises during a brief motor test. | Gimbal (if applicable) | Check for smooth movement and ensure it’s securely mounted. |
| Camera | Verify lens clarity and ensure the camera is securely attached. Check the camera’s functionality through the app. | Airframe | Inspect the drone’s body for any damage, cracks, or loose parts. |
| GPS | Ensure GPS signal is strong and the drone is able to locate its position accurately. | Remote Controller | Check the battery level of the controller and verify that all buttons and sticks function correctly. |
Airspace Regulations and Restrictions
Understanding and adhering to local airspace regulations is non-negotiable. Flying without proper authorization can result in hefty fines, license suspension, or even criminal charges. Always check with your local aviation authority (e.g., FAA in the US, CAA in the UK) for specific regulations in your area.
For example, flying near airports or restricted areas is strictly prohibited. Failure to comply can lead to collisions with aircraft, disruption of air traffic, and severe legal consequences. Additionally, many countries have specific regulations regarding drone registration and operator certification.
Safety Briefing for New Drone Operators
A comprehensive safety briefing should be provided to all new drone operators. This briefing should cover emergency procedures and potential hazards.
- Emergency Procedures: Explain procedures for handling loss of signal, low battery warnings, and unexpected malfunctions. Emphasize the importance of initiating a safe return-to-home (RTH) procedure in such situations.
- Potential Hazards: Discuss potential hazards such as collisions with objects, uncontrolled crashes, and injuries caused by malfunctioning propellers. Stress the importance of maintaining a safe distance from people and property during operation.
- Weather Considerations: Highlight the dangers of flying in adverse weather conditions, including strong winds, rain, and snow. Explain how these conditions can affect flight stability and control.
Drone Controls and Basic Operation
Understanding the controls and basic operation of your drone is essential for safe and effective flight. This section will guide you through the fundamental aspects of drone operation.
Drone Remote Control
Most drone remotes utilize two joysticks, several buttons, and switches to control various aspects of the drone’s flight. Understanding their functions is crucial for safe operation.
Successfully piloting a drone involves understanding its controls and mastering basic flight maneuvers. Learning the fundamentals is crucial before tackling more advanced techniques, and a great resource for this is available at how to operate a drone. From there, you can progress to more complex operations like aerial photography or videography, ensuring safe and responsible drone usage at all times.
- Left Joystick (Yaw and Throttle): Controls the drone’s altitude (throttle) and rotation (yaw).
- Right Joystick (Pitch and Roll): Controls the drone’s forward/backward (pitch) and left/right (roll) movements.
- Return-to-Home (RTH) Button: Initiates an automated return to the takeoff point.
- Emergency Stop Button: Cuts power to the motors, causing an immediate descent.
- Camera Control Buttons: Allow adjustments to camera settings, such as taking photos or recording videos.
- Flight Mode Switch: Selects different flight modes, affecting stability and maneuverability.
Flight Modes
Different flight modes offer varying levels of stability and control, catering to different skill levels and flight scenarios.
- Beginner Mode (or GPS Mode): Limits the drone’s speed and responsiveness, making it easier to control for beginners. It often includes features like automatic stabilization and obstacle avoidance.
- Sport Mode: Enables faster speeds and more aggressive maneuvers, suitable for experienced pilots.
- Manual Mode: Provides full manual control over the drone, requiring significant skill and experience.
Taking Off, Hovering, and Landing

This step-by-step guide Artikels the process of safely taking off, hovering, and landing a drone.
- Takeoff: Slowly increase the throttle using the left joystick. The image shows the drone’s propellers spinning gently as it lifts off the ground, demonstrating a smooth and controlled ascent. The drone remains stable and maintains a level orientation during this initial phase.
- Hovering: Once airborne, gently adjust the joysticks to maintain a stable hover at a safe altitude. The image displays the drone’s propellers spinning gently during a stable hover, highlighting the even distribution of lift. The drone remains perfectly still, indicating precise control.
- Landing: Slowly decrease the throttle using the left joystick, allowing the drone to descend gently. The image shows the drone smoothly descending towards the ground, maintaining its stability and orientation until it touches down. The propellers slow down gradually, ensuring a soft landing.
Navigating and Maneuvering the Drone
Precise maneuvering is key to successful drone operation. This section details techniques for controlling the drone’s movement in various directions.
Precise Maneuvering Techniques
Controlling the drone involves precise use of the joysticks to achieve forward, backward, sideways, and rotational movements. Smooth and controlled inputs are essential to avoid abrupt movements.
- Forward/Backward: Use the right joystick’s forward/backward movement to control the drone’s pitch.
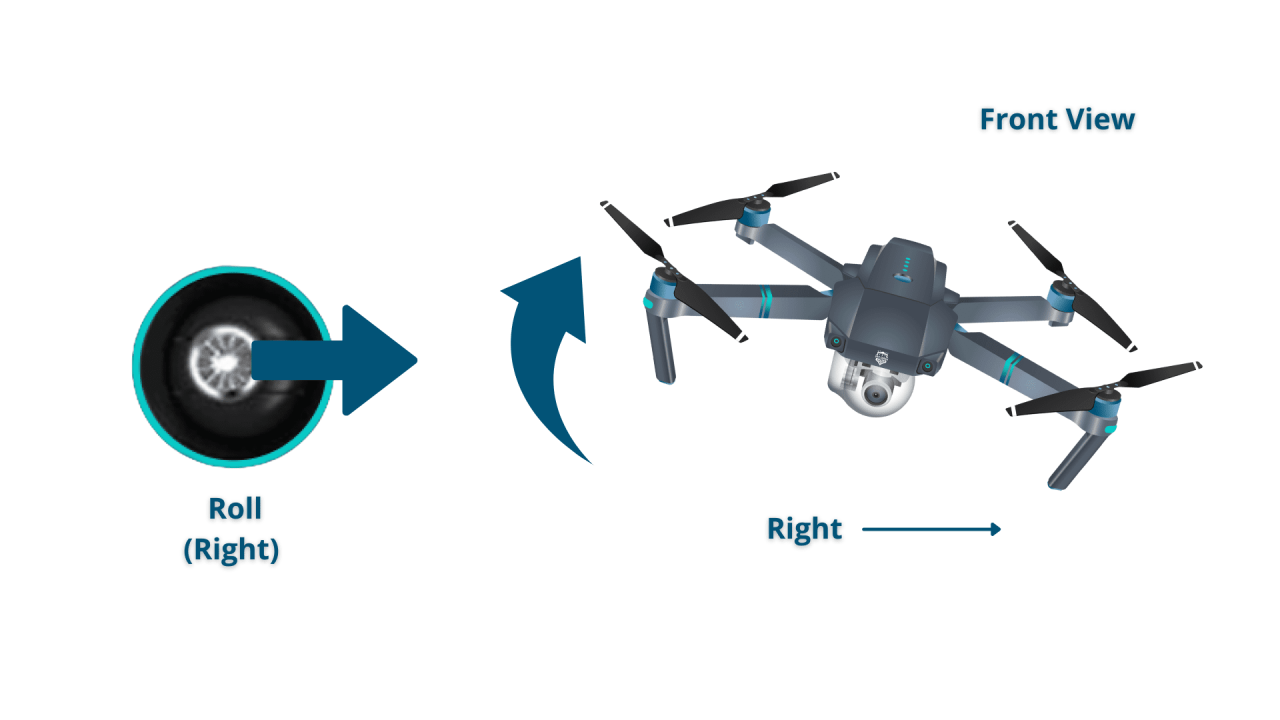
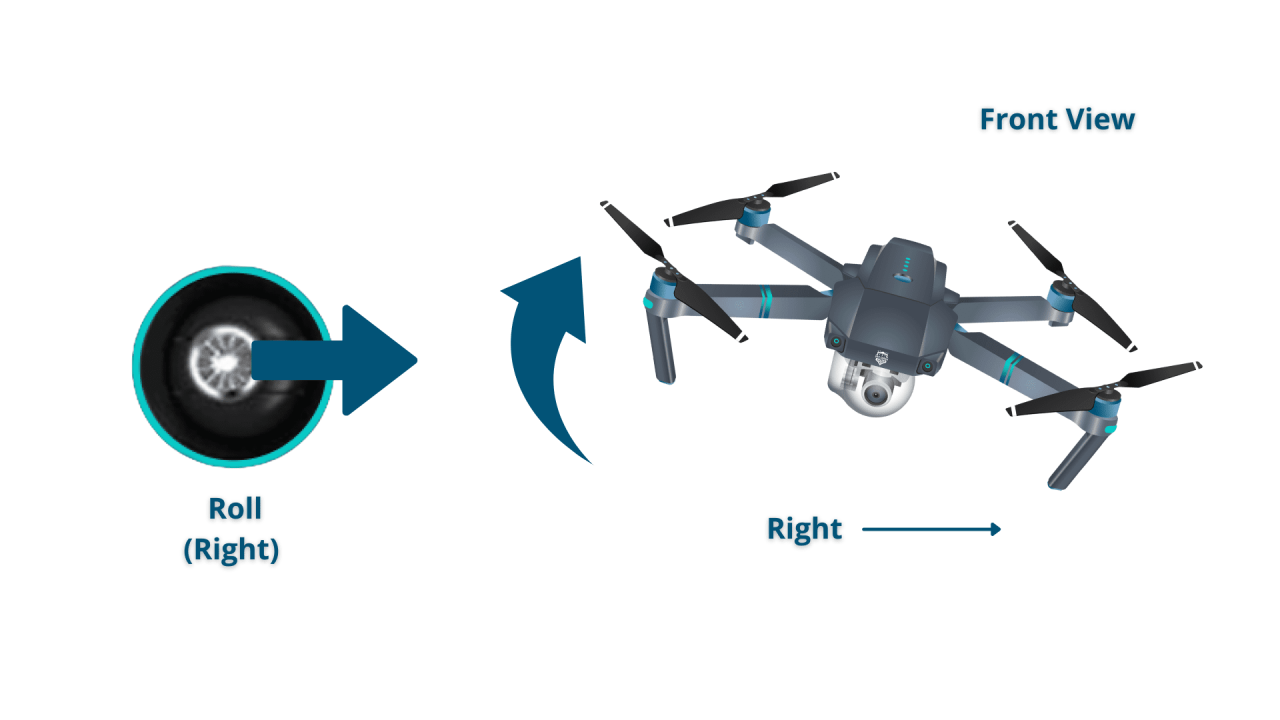
- Sideways (Lateral): Use the right joystick’s left/right movement to control the drone’s roll.
- Rotational (Yaw): Use the left joystick’s left/right movement to control the drone’s yaw (rotation).
GPS and Navigational Aids

GPS and other navigational aids enhance flight path planning and drone positioning. Most drones utilize GPS to maintain their location and return to the home point.
- GPS Assisted Flight: GPS enables features like Return-to-Home (RTH), which automatically returns the drone to its starting point in case of signal loss or low battery.
- Waypoints: Some drones allow setting waypoints, creating a pre-programmed flight path for automated navigation.
Controlling Altitude and Speed
Drone altitude and speed can be controlled using the throttle stick and adjusting flight settings. Smooth adjustments are crucial for maintaining stability and preventing abrupt changes.
- Throttle Stick: Controls the drone’s vertical speed (ascent and descent).
- Flight Settings: Many drones offer settings to adjust maximum speed and responsiveness.
Advanced Flight Techniques: How To Operate A Drone
This section covers advanced flight maneuvers that require more skill and practice.
Specific Flight Maneuvers
Advanced maneuvers require precise control and understanding of the drone’s response to joystick inputs.
- Circling: Requires coordinated use of the yaw and throttle sticks to maintain a consistent radius and altitude.
- Figure-Eights: Demands precise control of pitch, roll, and yaw to execute smooth and controlled turns.
- Precise Hovering: Maintaining a perfectly still position requires delicate adjustments to all joystick inputs to counteract any external forces like wind.
Tips for Smooth and Controlled Movements
Smooth and controlled movements are essential for capturing high-quality footage and preventing accidents.
- Avoid Abrupt Movements: Gentle joystick inputs minimize jerky movements and ensure smoother footage.
- Practice Regularly: Consistent practice enhances control and coordination.
- Understand Wind Conditions: Adjust flight strategy to compensate for wind.
Using Waypoints for Automated Maneuvers
Waypoints enable the creation of complex, automated flight paths for intricate aerial shots.
- Waypoint Planning: Many drone apps allow setting waypoints to define the drone’s flight path.
- Automated Flight: Once waypoints are set, the drone autonomously follows the path, freeing the pilot to focus on camera operation.
Drone Camera Operation and Photography
Capturing high-quality images and videos requires understanding drone camera settings and composition techniques.
Adjusting Camera Settings
Camera settings like shutter speed, aperture, and ISO significantly impact image quality. Understanding these settings allows for creative control over exposure and depth of field.
- Shutter Speed: Controls motion blur; faster speeds freeze motion, while slower speeds create blur.
- Aperture: Controls depth of field; wider apertures create shallow depth of field (blurred background), while narrower apertures create greater depth of field (everything in focus).
- ISO: Controls sensitivity to light; higher ISO values are useful in low-light conditions but can introduce noise (grain).
Camera Modes, How to operate a drone
Different camera modes cater to various shooting styles and applications.
- Photo Mode: For capturing still images.
- Video Mode: For recording video footage.
- Timelapse Mode: For creating time-lapse sequences by capturing images at set intervals.
Framing Shots and Composing Images
Effective composition is key to compelling aerial photography. Consider these factors when framing shots.
- Perspective: Utilize the drone’s ability to capture unique perspectives not possible from ground level.
- Lighting: Shoot during the “golden hour” (sunrise and sunset) for optimal lighting.
- Subject Matter: Choose interesting subjects and compose the shot to highlight them effectively.
- Rule of Thirds: Place key elements along imaginary lines that divide the frame into thirds, both horizontally and vertically.
- Leading Lines: Use natural lines (roads, rivers) to draw the viewer’s eye to the main subject.
Battery Management and Charging
Proper battery management is crucial for extending the lifespan of your drone batteries and preventing safety hazards.
Safe Charging and Storage Procedures
Always charge drone batteries in a well-ventilated area, away from flammable materials. Use only the manufacturer-recommended charger and follow the instructions carefully.
- Use Approved Charger: Using an incorrect charger can damage the battery or cause a fire.
- Avoid Overcharging: Overcharging can reduce battery lifespan and create a fire hazard.
- Store Properly: Store batteries in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight.
Factors Influencing Flight Time
Several factors affect how long your drone can fly on a single charge.
- Battery Capacity: Larger capacity batteries provide longer flight times.
- Flight Style: Aggressive flying consumes more power than gentle flying.
- Environmental Conditions: Wind, temperature, and altitude affect flight time.
Managing Multiple Batteries
For extended flights, managing multiple batteries is essential. Always have a few extra fully charged batteries on hand.
- Keep Track: Use a system to keep track of which batteries are charged and which need charging.
- Rotate Batteries: Rotate batteries to ensure even wear and tear.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
This section addresses common drone malfunctions and provides troubleshooting steps.
Common Drone Malfunctions and Troubleshooting
Knowing how to troubleshoot common issues can save you time and frustration.
| Malfunction | Troubleshooting Steps | Malfunction | Troubleshooting Steps |
|---|---|---|---|
| Loss of Signal | Check the distance from the drone, ensure no interference, and check the controller and drone batteries. | Low Battery | Land immediately, charge the battery, and consider using a higher capacity battery in the future. |
| Motor Failure | Inspect the motor for damage, check the propellers, and ensure proper connections. Consider contacting support if the problem persists. | GPS Issues | Ensure the GPS signal is strong, move to an open area, and restart the drone. |
Drone Maintenance
Regular maintenance extends the lifespan of your drone and ensures optimal performance.
| Maintenance Task | Frequency | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inspect Propellers | Before each flight | Check for cracks, damage, or debris. | Replace damaged propellers immediately. |
| Clean Drone Body | After each flight | Remove dirt, dust, and debris. | Use a soft cloth and avoid harsh chemicals. |
| Check Gimbal (if applicable) | Weekly | Ensure smooth movement and proper function. | Tighten any loose screws. |
| Check Battery Health | Monthly | Monitor battery voltage and capacity. | Replace batteries as needed. |
Interpreting Error Messages
Understanding error messages displayed on the remote control or app is crucial for diagnosing and resolving issues.
- Consult the Manual: Your drone’s manual provides explanations for various error codes.
- Online Resources: Search online for solutions to specific error messages.
- Contact Support: If you cannot resolve the issue, contact the drone manufacturer’s support team.
Mastering drone operation is a rewarding journey, combining technical skill with creative expression. By understanding the fundamentals of pre-flight preparation, flight controls, navigation, and camera operation, you unlock the potential to capture breathtaking visuals and explore the world from a unique perspective. Remember to prioritize safety and always adhere to local regulations. With practice and dedication, you’ll transform from a novice pilot into a confident aerial photographer and explorer.
Soar safely and enjoy the journey!
FAQ Guide
What type of drone is best for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones with GPS and beginner modes are ideal for starting. Look for models with good stability and features that assist in safe operation.
How do I register my drone?
Registration requirements vary by country and region. Check your local aviation authority’s website for specific rules and procedures.
Understanding drone operation involves familiarizing yourself with its controls and safety protocols. Learning how to navigate and maneuver the device effectively is crucial, and a great resource for this is the comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone. This will ensure you can safely and efficiently operate your drone, maximizing its potential while adhering to all regulations.
What should I do if I lose signal with my drone?
Most drones have a “return-to-home” function. Activate this immediately. If unavailable, attempt to regain signal gradually, moving closer while keeping visual contact.
How often should I calibrate my drone’s compass?
Compass calibration should be performed before each flight, especially if the drone has been moved significantly or exposed to magnetic interference.